Stokes Law
Stokes Law: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Stokes' Law, Applications of Stokes' Law, Velocity of Rain Drops, Velocity of Spherical Ball in Viscous Medium, Viscous Force on Spherical Bodies and, Terminal Velocity of Spherical Ball
Important Questions on Stokes Law
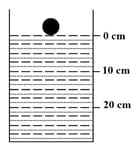
A spherical ball of density and radius is dropped into a tube containing a viscous fluid, filled up to the mark as shown in the figure. Viscosity of the fluid = and its density = . Assume the ball reaches a terminal speed by the mark. Find the time taken by the ball to traverse the distance between the and mark. [ = acceleration due to gravity = ]
A spherical ball of radius and density falls freely under gravity through a distance before entering a tank of water. If after entering the water the velocity of the ball does not change, find . The viscosity of water is .
The terminal velocity of copper ball of radius falling through a tank of oil at is . If viscosity of the oil at is and density of copper is Then density of the oil will be
Eight equal drops of water are falling through air with a steady speed of . If the drops coalesce, the new velocity is:-
An air bubble of diameter rises steadily through a solution of density at the rate of . The co-efficient of viscosity of the solution (neglect density of air) is ________ Pas (given, ).
A ball of mass and radius and density is dropped in a liquid of density . After moving for sometime, the speed of the ball becomes constant and equal to . The coefficient of viscosity of the liquid is
A liquid drop of mass and radius is falling from great height. Its velocity is proportional to
What is the terminal velocity of a rain drop of radius ?
[Note that the coefficient of viscosity of air is , density of water is . Use and density of air can be neglected in comparison with density of water]
Two solid spherical balls and of density have radius of and respectively. Ball is dropped in a liquid of density and viscosity and ball is dropped in another liquid of density and viscosity . The terminal velocity of ball is times that of ball . The value of is
A force acts on a particle whose mass is and whose velocity is at . It's terminal velocity (velocity after a long time) is:
The velocity of a small ball of mass and density , when dropped in a container filled with glycerine, becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is , then the viscous force acting on the ball, will be
A water drop of radius falls in a situation where the effect of buoyant force is negligible. Co-efficient of viscosity of air is and its density is negligible as compared to that of water . Terminal velocity of the water drop is
(Take acceleration due to gravity )
The terminal velocity of the spherical rain drop depends on the radius of the spherical rain drop as
A piece of iron bob is dropped in a very long column of water. What type of motion will be experienced by the bob near the bottom of the water column ?
How is the viscosity of a highly viscous liquid determined by measuring the terminal velocity.
Describe an experiment to determine the terminal velocity.
"Rain drops falling under gravity do not acquire very high velocity". Why ?
A drop of water of radius is falling through a medium whose density is and coefficient of viscosity . Find the terminal velocity of the drop.